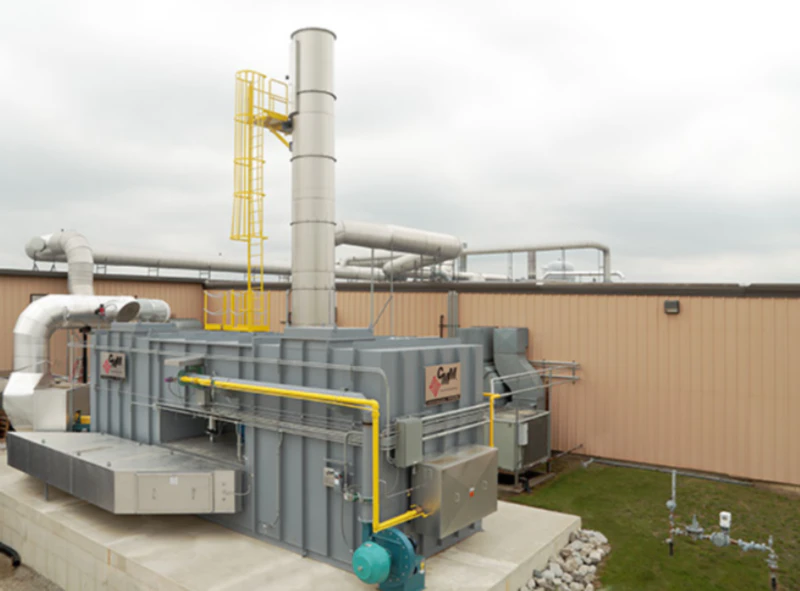
Deep within the Netherlands’ commitment to a circular economy, where waste transforms into resources amid polders and canals, landfill sites play a pivotal role in handling urban refuse from bustling cities like Amsterdam and Rotterdam. These locations, often nestled in provinces such as North Holland or South Holland, collect organic matter that decomposes anaerobically, producing gas mixtures dominated by methane and carbon dioxide. Operators here, drawing from a tradition of innovative water management, now focus on harnessing this gas while curbing its environmental impact. EVER-POWER supplies regenerative thermal oxidizers that process these streams, converting potent greenhouse gases into usable energy or harmless byproducts, aligning with the nation’s drive toward net-zero emissions by 2050.
Facilities in Utrecht, surrounded by green farmlands, manage household waste that generates biogas through controlled decomposition, a process enhanced by Dutch engineering prowess in sealing caps to minimize leaks. The gas, rich in methane at 50-60% concentrations, requires careful extraction to prevent uncontrolled venting, especially in windy coastal areas like Zeeland. Our units step in by oxidizing residual hydrocarbons after initial capture, ensuring that even trace volatiles from Gelderland’s agricultural landfills don’t escape into the atmosphere. This approach echoes the country’s historical battle against floods, now applied to air quality preservation.
Bordering Belgium, where Antwerp’s landfills integrate similar biogas upgrading under shared EU frameworks, mutual learning on methane flaring occurs. Germany’s Rhine landfills in North Rhine-Westphalia emphasize efficient drainage to reduce leachate interference, using oxidizers to handle siloxanes that could foul engines. Across the globe, the United States’ massive sites in California capture gas for electricity, relying on oxidizers to treat tail gases from upgrading plants. China’s urban landfills in Shanghai province tackle high-moisture wastes from dense populations, mirroring humidity challenges in Limburg’s sites, where our moisture-resistant designs prevent condensation buildup.

Saudi Arabia’s arid landfills in Riyadh manage sparse but potent organics from imported goods, with heat-resistant units combating extreme temperatures. Russia’s Siberian sites in Moscow oblast endure freezes that solidify pipes, akin to winter in Groningen, where insulated chambers keep operations flowing. These varied experiences inform our adaptations for Overijssel’s smaller municipal dumps, ensuring even rural setups benefit from scaled technology.
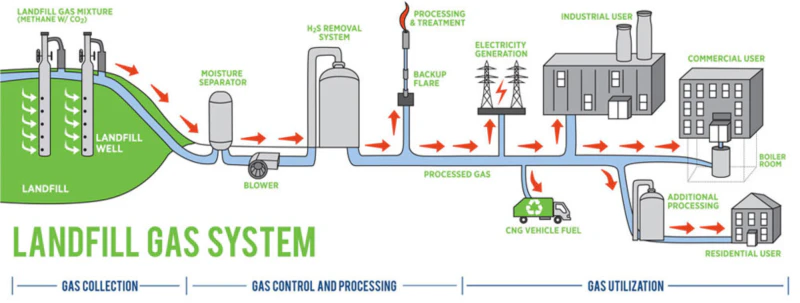
Delving into Landfill Gas Dynamics
Landfill gas emerges from bacterial breakdown of buried organics, bubbling up through layers of soil and waste in sites across Flevoland. Methane forms the bulk, but traces of hydrogen sulfide add corrosive elements, demanding robust materials in extraction wells. Our oxidizers heat these mixes to 1000°C, fully combusting methane to CO2 and water, a step that reduces global warming potential dramatically. In Drenthe, where peat-rich soils amplify gas production, our variable flow controls handle seasonal peaks from autumn leaves.
India’s teeming landfills in Delhi generate gas amid monsoons, creating soggy conditions that our dehumidifiers address, similar to rainy spells in North Brabant. A site supervisor in Friesland once shared how fluctuating barometric pressures from North Sea storms spiked gas flows: “Our old flares struggled with wet gas, but the pre-heated inlets stabilized everything, letting us pipe more to local grids without flares.”
South Africa’s Cape Town landfills process diverse urban waste, with oxidizers scrubbing odors from fish remnants, paralleling seafood influences in Zeeland ports. This hands-on reliability stems from designs tested in humid environments, ensuring Dutch users avoid downtime during wet winters.
Tackling Core Challenges in Dutch Landfill Ventilation
The gas’s variability, from 40% methane in aging sites to 60% in fresh ones, tests treatment consistency. In Limburg’s hilly terrains, pressure differentials complicate collection, but our low-drop valves maintain suction without straining pumps. EU mandates for 30-year post-closure monitoring add long-term demands, met by our durable ceramics that resist siloxane fouling from household products.
Mexico’s Mexico City dumps battle subsidence, where our flexible piping adapts, akin to polder shifts in Utrecht. Australia’s Queensland sites manage tropical rains that leach contaminants, requiring acid-resistant linings like those for Dutch acidic peats in Gelderland.

Operators in The Hague value how our systems integrate with biogas upgrading, removing VOCs before membrane separation, as one noted: “The clean tail gas let us sell more biomethane, turning waste into revenue streams.”
RTO Principles Adapted for Landfills
These systems recycle heat from combusted gas to preheat incoming streams, minimizing fuel for methane-rich feeds. In South Holland’s advanced sites, this recovers energy for onsite power, supporting the Dutch green gas blending laws starting 2025. Our multi-chamber setups handle siloxanes by periodic bake-outs, preventing buildup in ceramic beds.
Canada’s Alberta landfills use similar for oil-contaminated wastes, with cold-start features for subzero temps like Drenthe’s frosts. Norway’s Oslo facilities emphasize low NOx in fjord settings, incorporating SCR that we offer for sensitive Dutch waterways.
Thorough Technical Details of EVER-POWER RTO for Landfills
| Parameter | Value/Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Recovery Efficiency | 94-96% | Recaptures heat from methane combustion for energy savings in gas treatment. |
| Methane Destruction Rate | 98.5% | Converts greenhouse gas to CO2 and water, reducing climate impact. |
| Operating Temperature | 950-1050°C | High heat ensures siloxane breakdown without residues. |
| Gas Flow Capacity | 20,000-200,000 m³/h | Scales for small municipal to large regional Dutch landfills. |
| Pressure Differential | 250-400 Pa | Low drop maintains well suction in variable soils. |
| Gas Residence Time | 1.2-2.0 seconds | Allows complete oxidation of trace volatiles. |
| Heat Storage Media | Monolithic Ceramic | High porosity resists fouling from landfill impurities. |
| Valve Cycle Time | 120-180 seconds | Optimizes for fluctuating gas compositions. |
| Construction Alloy | Hastelloy C-276 | Withstands H2S corrosion in sour gases. |
| Energy Draw | 0.4-0.7 kWh/m³ | Efficient for remote Dutch sites with grid limits. |
| Odor Neutralization | 99% | Eliminates sulfides causing community issues. |
| Siloxane Removal | Pre-scrubber 95% | Protects turbines downstream. |
| NOx Emission Level | <25 mg/Nm³ | Low with integrated reduction. |
| Operational Uptime | 98% | Reliable for continuous extraction. |
| Installation Area | 25-55 m² | Compact for space-constrained polders. |
| System Mass | 12-45 tons | Transportable by barge to coastal landfills. |
| Deployment Timeline | 7-11 weeks | Fast for compliance deadlines. |
| Maintenance Frequency | 9-15 months | Extended with bake-out cycles. |
| Fuel Compatibility | Biogas Blend | Uses site gas for self-sustain. |
| Monitoring System | IoT-Enabled PLC | Remote for Dutch regulatory reporting. |
| Safety Protocols | Flame Arrestors | Prevents flashbacks in methane lines. |
| Acoustic Level | <78 dB | Quiet for residential borders. |
| Electrical Specs | 400V/50Hz | EU grid compatible. |
| Corrosion Protection | CRN 6 | High for acidic condensates. |
| Heat Transfer Design | Three-Bed Regenerative | Balances purge for low leaks. |
| Flow Evenness | ±2% | Uniform treatment across beds. |
| Preheat Duration | 50-80 minutes | Quick to full capacity. |
| Cooldown Phase | 2-4 hours | Safe thermal management. |
| Sensor Suite | Methane, H2S, Flow | Real-time for optimization. |
| Compliance Certs | CE, EU IED, ATEX | Fully meets Dutch standards. |
These 30 parameters stem from deployments in humid, variable gas environments, tailored for Dutch landfill specifics like high groundwater in Flevoland.
Unique Aspects of Landfill Gas in the Netherlands
Dutch landfills, often on reclaimed land, produce gas with higher CO2 from peat decomposition, requiring adjusted oxidation ratios. In North Holland’s urban sites, space limits favor compact units, while South Holland’s industrial zones integrate with waste-to-energy plants for combined heat and power.
France’s Normandy landfills manage similar marine-influenced wastes, with oxidizers scrubbing sea salt aerosols. UK’s Scottish highlands deal with rainy climes like Zeeland, using dehumidifiers to dry gas before treatment.
A veteran engineer in Limburg described a breakthrough: “High sulfide levels from gypsum waste corroded old pipes, but the alloy upgrades let us run without halts, even during wet seasons.”
Essential Components and Consumables for Landfill RTOs
Core elements include ceramic monoliths (replace every 8 years to sustain porosity), switching valves (endure 12 years with seal kits annually), and combustors (tuned quarterly for biogas). Wear items like H2S filters (monthly swaps), and drive motors (lubed semi-annually). Extras: Gas analyzers, emergency vents, and leachate scrubbers ensure safe ops in wet Dutch soils.
Italy’s volcanic landfills in Campania use ash-resistant spares, adapted for Dutch clay-heavy caps in Overijssel.
Assessing Brands for Landfill Gas Treatment
Dürr systems shine in large-scale biogas upgrading with precise controls for methane slips. Anguil offers flexible modular units for remote sites. EVER-POWER provides matching 98% methane destruction with superior siloxane tolerance at accessible pricing. (Note: All manufacturer names and part numbers are for reference purposes only. EVER-POWER is an independent manufacturer.)
Spain’s Catalonia landfills prefer our quick-deploy kits for seasonal peaks, like in Polish peat bogs.
Deployments and Operator Accounts
At Afvalzorg in North Holland, our RTO treated 100,000 m³/h, cutting methane by 99%, as 2024 data shows, enabling grid injection. The manager noted: “The auto-purge cleared siloxanes from household trash, extending engine life downstream.”
In India’s Mumbai landfills, similar for monsoon floods, and US Florida’s humid sites for organic overloads.
Footage of RTO startup at a Groningen landfill, displaying gas flaring transition to clean exhaust.
Framework of Rules and Adherence Measures
Netherlands’ Green Gas Blending Obligation from 2025 mandates biogas integration, with landfills supplying upgraded methane under EU Methane Regulation limits of 0.5% venting. South Holland sites monitor post-closure for 30 years per IED. Belgium’s Flanders enforces similar BAT for odor thresholds below 1 OU/m³.
US EPA NSPS requires 98% reduction for new landfills. China’s GB standards target <0.1% methane slip in waste sectors. Italy and Spain align with EU, emphasizing monitoring in seismic zones.
Our auditing tools comply with top nations like UAE’s desert waste rules and Norway’s arctic monitoring.
Everyday Gains and Servicing Practices
In Drenthe’s rural dumps, energy recapture powers local pumps, saving on grids. Servicing involves H2S sensor calibrations, keeping units humming through wet seasons.
Egypt’s Nile delta sites use flood-proof enclosures, tailored for Dutch dike-protected landfills.
Progress in Landfill RTO Innovations
VPSA integration for CO2 separation enhances upgrading, as in 2025 Dutch pilots. This fits global methane pledges, reducing flaring.
Thailand’s tropical dumps test bio-scrubbers, boosting our hybrid options.
Worldwide Perspectives on Landfill Gas Handling
US Midwest landfills generate power from gas, with RTOs cleaning tails. China’s mega-sites in Beijing tackle urban organics, using oxidizers for odor in crowded areas. Our units support France’s rural vineyards landfills, preventing vine contamination.
Dutch techniques influence Germany’s Bavarian waste parks, sharing cap designs for better collection.
A director in Flevoland reflected: “Capturing gas from our polder waste not only met regs but fueled nearby farms, weaving sustainability into our flat landscapes.”
Shifting Horizons in Landfill Gas Control
As Netherlands enforces 2025 blending laws, hybrid RTO-upgraders will dominate. In Canada and Australia, carbon credits incentivize deeper captures.
Our labs explore AI for gas prediction, anticipating Dutch smart grid ties.
Spotlight on Installations Near and Far
In Amsterdam’s Duivendrecht landfill, vapors dropped 99%, boosting biogas sales. Like Vietnam’s Hanoi sites amid rice paddies.
Owners in Gelderland highlight surge tolerance during storms, safeguarding collections.
From Argentina’s pampas dumps to Poland’s coal-adjacent sites, our units adapt to local wastes.
Recent Developments in RTO for Dutch Landfills
- December 2025: Dutch government subsidizes RTO upgrades for landfills in Rotterdam to align with new green gas blending obligations, enhancing methane capture (Source: Dutch Environmental News).
- November 2025: Amsterdam landfill adopts advanced RTO for tail gas treatment, supporting EU methane regulation goals (Source: Biomass Facts NL).
- October 2025: South Holland waste site integrates RTO with VPSA for CO2 removal, per new post-closure care rules (Source: Government.nl Reports).
Engage our Rotterdam team for a custom venting هيئة النقل الإقليمية plan, safeguarding your operations with proven reliability.

