Introduction: Why is RTO Technology Reshaping Industrial Exhaust Gas Treatment Standards?
Against the backdrop of increasingly stringent environmental regulations and “dual-carbon” goals, industrial volatile organic compounds (VOCs) treatment has become a critical challenge for the sustainable development of manufacturing industries. Traditional treatment technologies such as activated carbon adsorption and catalytic combustion are gradually revealing limitations in treatment efficiency, operating costs, and energy consumption. Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer (RTO), as an efficient, energy-saving, and reliable end-of-pipe VOCs treatment technology, is becoming the preferred solution for industries such as petrochemicals, printing and coating, pharmaceuticals, and electronics.
This article provides a comprehensive practical guide to RTO technology from four dimensions: technical principles, energy efficiency advantages, application scenarios, and selection considerations.
Part One: Core Principles and Structural Innovations of RTO Technology
What is RTO? Analysis of Three Core Components
The core design concept of Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer (RTO) is energy recycling. Compared to direct thermal oxidation, RTO utilizes regenerative ceramic beds to achieve exhaust gas preheating and purified gas waste heat recovery, increasing thermal energy utilization efficiency to over 95%.
System Composition Diagram: [Exhaust Gas Inlet] → [Diverter Valves] → [Regenerative Ceramic Bed A (Preheating Zone)] → [Combustion Chamber (760-850°C)] ↓ [Purified Gas Outlet] ← [Regenerative Ceramic Bed B (Cooling Zone)] ← [Diverter Valves]
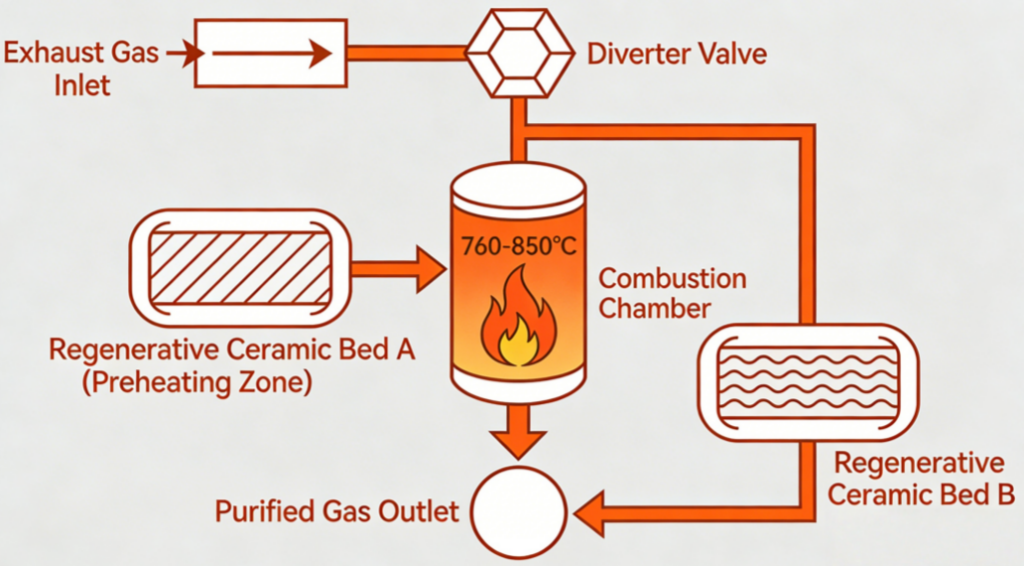
Technical Parameter Benchmarks
- Treatment Efficiency: ≥98% (can reach over 99% under well-designed conditions)
- Operating Temperature: 760-850°C (adjustable based on exhaust gas composition)
- Heat Recovery Efficiency: Typical value ≥95%, maximum up to 97%
- Pressure Drop Range: 2.5-3.5 kPa (can be reduced below 2.0 kPa with optimized design)
- Switching Cycle: Adjustable 30-180 seconds, depending on exhaust concentration and flow rate
Technology Comparison: RTO vs. RCO vs. TO
| Technology Type | Treatment Efficiency | Operating Temperature | Fuel Consumption | Suitable VOCs Concentration | Investment Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| هيئة النقل الإقليمية | 98-99% | 760-850°C | Very Low (self-sustaining concentration 3g/m³) | Broad Spectrum (1-10g/m³) | Medium-High |
| RCO | 95-98% | 300-400°C | Low (catalyst required) | Medium-Low Concentration | High |
| Direct TO | 90-95% | 650-800°C | High (no heat recovery) | High Concentration | Low |
Part Two: Energy Efficiency Advantages and Economic Benefit Analysis of RTO
Energy Self-Sustaining Threshold: When Can RTO Achieve “Zero Fuel” Operation?
Core Formula: Self-sustaining concentration = (System heat loss) / (VOCs calorific value × Heat recovery efficiency)
For a typical three-bed RTO system:
- With 95% heat recovery efficiency, self-sustaining concentration is approximately 1.5-2.5 g/m³
- With 97% heat recovery efficiency, self-sustaining concentration can be reduced to 1.0-1.8 g/m³
This means when VOCs concentration in exhaust gas reaches this threshold, the system can operate continuously with almost no auxiliary fuel.
Five-Year TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) Comparison Model
Taking a coating production line with 30,000 Nm³/h treatment capacity as an example:
| Cost Item | RTO System | Activated Carbon Adsorption + Catalytic Combustion | Savings Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | 1.8 million CNY | 1.2 million CNY | -50% |
| Annual Operating Cost (Electricity + Fuel) | 280,000 CNY | 520,000 CNY | +46% Savings |
| Annual Maintenance Cost | 80,000 CNY | 150,000 CNY (including activated carbon replacement) | +47% Savings |
| 5-Year Total Cost | 3.28 million CNY | 4.55 million CNY | +28% Total Savings |
| Carbon Emission Reduction (5 years) | 1,200 tons CO₂e | 750 tons CO₂e | +37% Reduction Advantage |
Key Insight: Although RTO has higher initial investment, operational savings within 3-4 years can compensate for the price difference, with significant long-term economic benefits.
Part Three: Industry Application Scenarios and Success Cases
Scenario 1: High-Concentration Complex Component Exhaust in Chemical Industry
Challenge: Large fluctuations in exhaust concentration (1-8g/m³), containing corrosive components such as chlorine and sulfur
RTO Solution:
- Use corrosion-resistant special ceramic regenerative materials
- Configure adaptive control system for concentration fluctuations
- Add quench tower pretreatment for acidic gases
Results: After installation at a pesticide intermediate factory, VOCs removal rate stabilized at 99.2%, with annual natural gas cost savings of 850,000 CNY.
Scenario 2: Large Air Volume, Low Concentration Exhaust in Printing and Packaging Industry
Challenge: Large air volume (50,000-100,000 Nm³/h), low concentration (0.5-1.5g/m³)
RTO Solution:
- Use rotary RTO to reduce equipment size
- Integrate zeolite rotor wheel for concentration enhancement (10-15 times concentration)
- Intelligent variable frequency control to adapt to production fluctuations
Results: After implementation at a flexible packaging enterprise, self-sustaining operation achieved at only 0.8g/m³ concentration, with annual electricity consumption reduced by 40%.
Scenario 3: Intermittent Emissions from Automotive Coating Lines
Challenge: Exhaust flow rate drops from 100% to 10% between production shifts, drastically reducing traditional RTO energy efficiency
Innovative Solution:
- Adopt multi-bed variable air volume RTO (such as five-bed design)
- Develop “sleep mode” algorithm, automatically shutting down some regenerative beds during low load
- Integrate with production MES system for predictive adjustment of operating parameters
Results: At an automotive factory, comprehensive energy consumption reduced by 35%, startup/shutdown cycles reduced by 70%, and equipment lifespan extended.

Part Four: Key Considerations for RTO Selection and Design (Procurement Guide)
Seven Core Selection Parameter Checklist
- Exhaust Gas Characteristic Analysis: Components, concentration range, humidity, particulate content
- Air Volume Confirmation: Consider peak, average values and future production expansion margin (recommended +20%)
- Heat Recovery Efficiency Target: ≥95% as baseline, 97% as high-performance indicator
- Valve Type: Butterfly valves (economical) vs. poppet valves (high sealing)
- Control System: PLC standard, recommend DCS or SCADA integration interface
- Compliance Requirements: Local emission standards (e.g., GB 16297), explosion-proof rating
- Space Limitations: Equipment dimensions, maintenance access, hazardous waste handling pathways
Five EEAT Dimensions for Supplier Evaluation
- Experience: Number of same-industry cases (require ≥3 success cases)
- Expertise: Whether providing pre-project services such as exhaust testing, process simulation
- Authoritativeness: Patent holdings, participation in standard development records
- Trustworthiness: Customer testimonials, third-party test report transparency
- Technical Capability: Independent R&D proportion, quality control of key components (e.g., ceramics, valves)
Part Five: Common Questions and Misconceptions Clarification
Q1: Is RTO Suitable for Exhaust Containing Silicones, Phosphorus, etc.?
Professional Answer: Exhaust containing silicon, phosphorus, metal compounds requires pretreatment. Silicones form SiO₂ deposits on ceramics at high temperatures. Recommendations:
- Add front-end scrubber or dry filter
- Use smooth-surface honeycomb ceramics
- Configure online ceramic bed cleaning system
Q2: How to Choose Between Two-Bed, Three-Bed, and Rotary RTO?
Selection Matrix:
- Two-Bed RTO: Continuous stable exhaust, concentration >2.5g/m³, limited budget
- Three-Bed RTO (Recommended): Fluctuating exhaust, pursuing ≥98% efficiency, industry mainstream
- Rotary RTO: Ultra-large air volume (>80,000 Nm³/h), space-constrained
Q3: How to Solve RTO’s “Hot Spot Migration” Problem?
Technical Solutions: Control bed temperature unevenness through:
- Optimized airflow distribution design
- Use of high thermal conductivity ceramic materials
- Regular thermal imaging inspection and maintenance
Part Six: Future Trends and Intelligent Upgrade Pathways
Digital RTO: From “Treatment Equipment” to “Energy Efficiency Management Center”
- Predictive Maintenance: Fault early warning through vibration, temperature, differential pressure sensors
- Digital Twin Optimization: Establish virtual models, real-time optimization of switching cycles and temperature settings
- Carbon Asset Visualization Management: Automatic calculation of VOCs reduction and carbon credits, generating ESG reports
- Cloud Platform Remote Operation and Maintenance: Centralized monitoring of multiple plant areas and remote expert diagnostics
Material Innovation Directions
- New Ceramic Materials: Increase thermal conductivity coefficient (from 1.2 to 2.0 W/m·K), reduce bed volume by 30%
- Phase Change Thermal Storage Materials: Develop paraffin-based composite materials, improve thermal storage density by 50%
- Coating Technology: Nanocoatings for anti-clogging, extending cleaning cycles to over 2 years
Conclusion: RTO is Not Just a Compliance Tool, But an Energy Efficiency Asset
With technological maturation and cost optimization, RTO has evolved from mere “end-of-pipe treatment equipment” to energy efficiency assets that generate significant economic benefits. Correct technology selection, professional engineering design, and intelligent operation and maintenance will enable your RTO system to continuously create environmental value and economic benefits over its 10-15 year lifecycle.
Immediate Action Recommendations:
- Conduct comprehensive exhaust testing and process analysis
- Invite 2-3 suppliers with same-industry experience to provide proposals
- Conduct small-scale pilot testing (if conditions permit) to verify treatment effectiveness
- Incorporate RTO into corporate ESG strategy, seek green credit support
Obtain Personalized Solutions
For detailed هيئة النقل الإقليمية technology solutions and economic benefit analysis tailored to your industry, please visit our website and contact our technical team for free consultation and case studies.
*This article is based on publicly available technical materials and industry practices. Specific applications should consult professional engineering companies. Data is for reference only, actual effects are subject to working conditions.*
