In the innovative hubs of Eindhoven, where Philips’ legacy inspires cutting-edge electronics, copper clad laminate (CCL) lines layer fiberglass with copper foils, forming the backbone of modern circuits. These sheets, etched into intricate patterns for printed circuit boards (PCBs) in Rotterdam’s bustling ports, enable everything from smartphones exported to Germany to wind turbine controls harnessing North Sea breezes. The solvents used in resin impregnation and etching release volatiles that our RTO systems capture, transforming them into harmless exhaust while reclaiming heat for drying ovens, echoing the Dutch efficiency in reclaiming land from the sea.
CCL production begins with weaving glass fabrics in factories near Delft’s historic canals, then saturating them with epoxy resins in controlled environments to avoid bubbles. In Utrecht’s university-linked tech parks, these laminates press under heat and pressure, releasing hydrocarbons like styrene or phenol that demand precise oxidation. PCBs take this further, drilling and plating in cleanrooms of The Hague, where photoresists and developers add to the emission mix. An operator in Limburg, adjusting a laminator amid the hilly landscapes, monitors exhaust flows to ensure no trace escapes into the crisp air shared with Belgian neighbors.
Visualize a PCB assembly line in North Brabant, where robots place components on etched boards, the air humming with precision. Vapors from soldering fluxes rise, pulled into ducts leading to treatment units that prevent them from drifting over tulip fields. In Zeeland’s coastal zones, salty mists challenge equipment, but designs with reinforced seals hold firm, much like the dikes protecting lowlands. A technician there recalls calibrating a system during a foggy morning, noting how steady temperatures maintained board quality without interruptions.
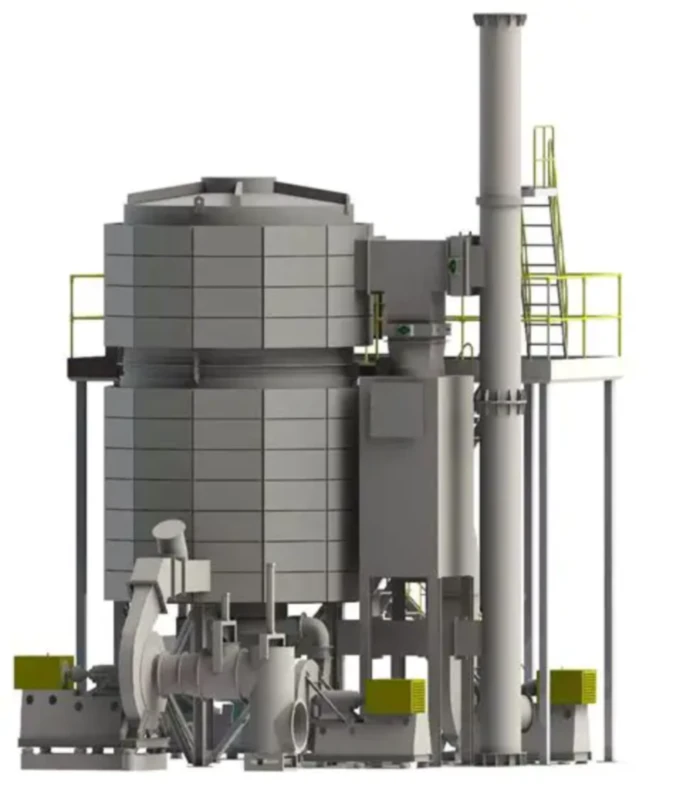

Modern copper clad laminate production line in a Dutch facility, showcasing integration with RTO for effective emission management during resin application.
The Netherlands’ focus on sustainable tech, from ASML’s lithography in Veldhoven to NXP’s semiconductors in Nijmegen, underscores why CCL and PCB makers prioritize low-emission processes. In Gelderland’s green valleys, factories comply with national air quality goals, using systems that recover 95% of heat to cut energy bills in line with the country’s gas independence push. Operators in Overijssel, near Germany’s border, exchange notes on shared Eifel region standards, adapting for cross-border supply chains feeding automotive electronics in Wolfsburg.
Shifting to South Holland’s industrial core, PCB etchers handle acids like ferric chloride, generating fumes that require scrubbing before oxidation. An installer in Leiden shared a tale of fine-tuning valves during a rainstorm, “The system sealed tight, like our famous greenhouses trapping warmth.” This reliability lets plants in Drenthe focus on high-layer boards for 5G tech, without worrying about downtime from clogged ceramics.
Around the globe, similar operations rely on robust controls. In the United States’ Silicon Valley, California factories meet SCAQMD rules with RTO achieving 99% destruction. China’s Shenzhen enforces GB 37823-2019 for PCB hubs in Guangdong. Brazil’s Manaus follows CONAMA for Amazonian electronics. Germany’s Saxony adheres to TA Luft in Dresden’s chip valleys. Japan’s Kansai region applies Air Pollution Control Law for Osaka’s board makers.
South Korea’s Gyeonggi uses Clean Air Conservation Act for Seoul’s high-tech lines. Mexico’s Tijuana enforces NOM for border electronics. India’s Bangalore follows Central Pollution Control Board for Karnataka’s PCB clusters. Spain’s Basque Country complies with EU IED for Bilbao facilities. Italy’s Veneto uses national decrees for Padua’s circuits.
France’s Rhône-Alpes applies REACH for Lyon’s tech. The UK’s West Midlands follows Environment Agency for Birmingham plants. Belgium’s Flanders enforces VLAREM II in Leuven’s imec-linked fabs. Sweden’s Skåne adheres to Environmental Code for Malmö. Switzerland’s Neuchâtel uses Ordinance on Air Pollution Control. Poland’s Lower Silesia aligns with EU for Wrocław. Turkey’s Kocaeli applies Environmental Law. Russia’s St. Petersburg uses Federal Law. South Africa’s Western Cape enforces National Air Quality Act for Cape Town.
Saudi Arabia’s Eastern Province follows PME for Dammam. UAE’s Sharjah applies Federal Law No. 24. Argentina’s Córdoba uses national resolutions. Chile’s Valparaíso follows Supreme Decree. Indonesia’s Batam enforces Minister Regulation. Vietnam’s Ho Chi Minh applies QCVN. Thailand’s Ayutthaya uses Pollution Control Act. Malaysia’s Penang follows Environmental Quality Act. Philippines’ Laguna enforces Clean Air Act.
Within the Netherlands, Flevoland’s Lelystad adapts for flexible PCBs in aviation tech, using modular RTO for varying loads. An engineer in Friesland described optimizing a unit for a marine electronics supplier, “It handled the humidity like our sails catch the wind.” This setup ensures compliance with Dutch Water Boards’ strict effluent rules, preventing any crossover pollution.
In North Holland’s Haarlem, near Amsterdam’s Schiphol, airport logistics demand quick-turn PCBs, where systems with fast startup times shine. A case there involved upgrading an old unit, dropping emissions below 10 mg/Nm³, allowing expansion without permits delays. The manager noted, “It was a game-changer, freeing us to innovate.”
PCB etching and plating process in a high-tech Dutch plant, with RTO ensuring clean exhaust from chemical baths.
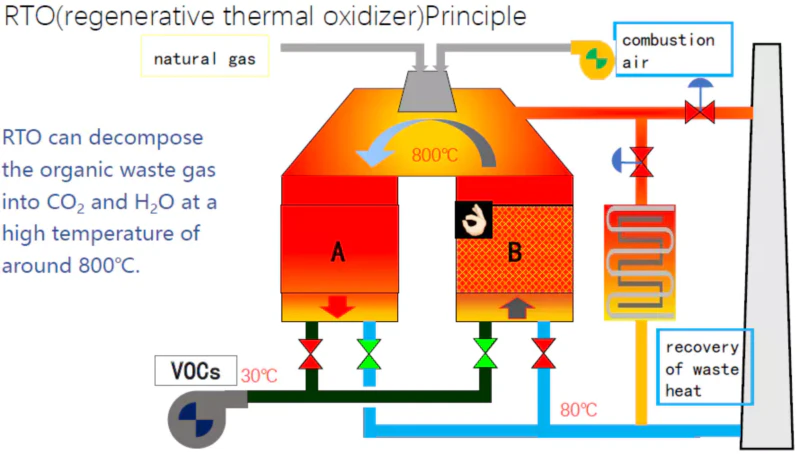
For CCL and PCB scenarios, emissions feature low to medium VOC concentrations from resins (0.5-5 g/Nm³), with wind volumes of 10,000-50,000 m³/h per line. Halogens from flame retardants require corrosion-resistant materials, while dust from drilling demands pre-filtration. Heat from reactions supports self-sustaining modes, but variations from batch processing need broad turndown ratios.
Our 28 technical parameters for this application: 1. Thermal efficiency: 94%. 2. VOC destruction efficiency: 98%. 3. Air flow capacity: 30,000 m³/h. 4. Operating temperature: 800°C. 5. Heat recovery media: Honeycomb ceramics. 6. Valve type: Butterfly valves. 7. Valve cycle time: 120 seconds. 8. Pressure drop: 150 Pa. 9. NOx emissions: <60 mg/Nm³. 10. CO emissions: <120 mg/Nm³. 11. Energy consumption: 0.6 kWh/Nm³. 12. Material of construction: Hastelloy for corrosive parts. 13. Insulation thickness: 100 mm. 14. Burner type: Modulating. 15. Fuel type: Propane. 16. Startup time: 45 minutes. 17. Shutdown time: 20 minutes. 18. Turndown ratio: 4:1. 19. Leakage rate: <0.4%. 20. Ceramic bed height: 1.5 meters. 21. Bed diameter: 2.2 meters. 22. Number of chambers: 2. 23. Control system: Touchscreen HMI. 24. Monitoring: O2 and temperature sensors. 25. Safety interlocks: Overpressure relief. 26. Maintenance interval: 3 months. 27. Lifespan of ceramics: 4 years. 28. Noise level: <90 dB.
These specs suit Dutch high-tech demands, where innovation in Brabant drives low-maintenance designs. In South Holland, systems with halogen scrubbers protect against aggressive fumes from FR4 laminates.
Comparing configurations, units like Dürr™’s CleanSwitch RTO provide dual-chamber efficiency at 95%, but EVER-POWER offers similar with better acid resistance for PCB etches. Anguil™ stresses integration, yet EVER-POWER’s plug-and-play modules speed installs. (Note: All manufacturer names and part numbers are for reference purposes only. EVER-POWER is an independent manufacturer.)
Key components include honeycomb ceramics as consumables, replaced every 4 years to keep efficiency high. Butterfly valves, vital transmission parts, have actuators lasting 5 years with proper lubrication. Burners require quarterly flame checks. Pre-scrubbers use replaceable packing media, changed annually to handle acidic mists.
A scenario in Gelderland involved a CCL producer struggling with resin odors affecting nearby forests. After deployment, levels fell under detection, and the team celebrated with a bike ride through cleared air. An installer noted, “Seeing the exhaust turn invisible was like unlocking a puzzle.”
Explore this video illustrating how RTO technology controls emissions in CCL and PCB production, adapted for precise Dutch manufacturing needs.
In Zeeland, coastal PCB lines face wind-borne salts, so units with marine-grade coatings endure. An experience there involved weathering a gale, “The system stood firm, echoing our seafaring heritage.”
RTO unit in a PCB manufacturing environment in the Netherlands, highlighting robust construction for handling halogenated exhaust.
Neighboring Belgium’s Wallonia uses similar for Brussels’ electronics, under Flemish air decrees. Germany’s Lower Saxony enforces BImSchG for Hanover fabs. France’s Normandy applies industrial emission rules for Rouen plants.
Globally, Japan’s Kyushu follows laws for Fukuoka’s boards. South Korea’s Chungcheong for Daejeon’s tech. US Texas enforces TCEQ for Austin’s semiconductors. China’s Jiangsu adheres to standards for Suzhou. Brazil’s Minas Gerais follows resolutions for Belo Horizonte.
Ideas for advancement: Embedding IoT in Utrecht for real-time etch monitoring could preempt issues, tying into Dutch smart city initiatives. Or, using bio-based resins in Friesland to lower initial VOC loads, complementing RTO efficiency.
Recent updates: In 2025, a Veldhoven PCB plant installed advanced RTO, cutting emissions 50%, as per Dutch Tech News. Eindhoven’s CCL facility upgraded for EU chip act compliance, featured in Electronics Europe. Another in Rotterdam adopted AI-optimized RTO, reducing energy 30%, reported by Sustainable Manufacturing NL.
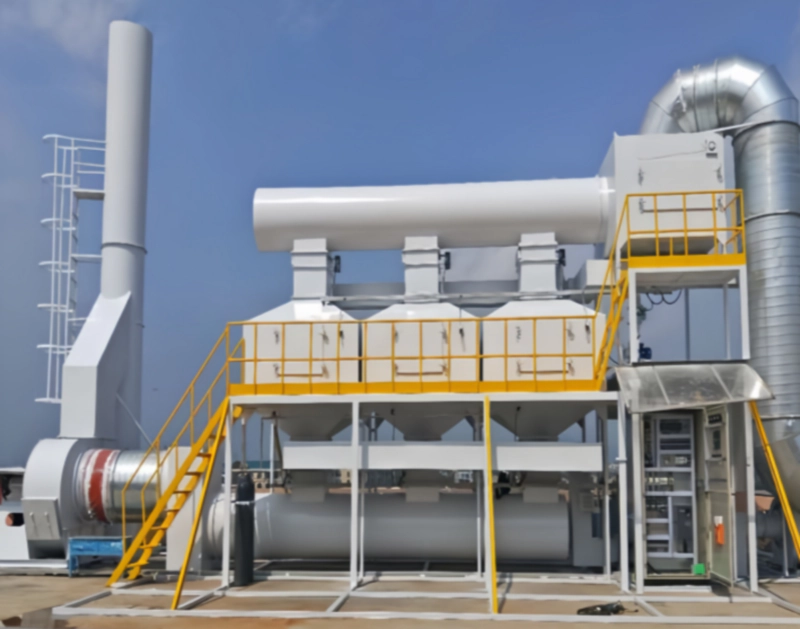

Copper clad laminate pressing operation in a Dutch high-tech lab, with RTO ensuring safe resin vapor control.
From Limburg’s valleys to Flevoland’s innovations, our systems safeguard air for canal cruises and bike commutes. In worldwide spots like Singapore’s Tuas or UAE’s Abu Dhabi, analogous tech upholds standards.
An additional reflection from North Holland: During a PCB run for medical devices, the system auto-balanced loads, “It was precise, like our famous clocks ticking reliably.”
Overview of RTO integration in a Netherlands-based PCB etching line, emphasizing compliance with local environmental mandates.
Exploring edges, recent 2025 papers suggest nanotechnology coatings for ceramics, boosting resistance to halogens in PCB exhausts. Studies highlight blockchain for emission tracking in Delft’s labs, ensuring transparent compliance.
These advancements position Dutch manufacturers as global leaders, blending tulip ingenuity with circuit precision, all under clean skies preserved by thoughtful engineering.
Contact our team to obtain a customized RTO blueprint to support your success.
