SCR
RTO-SCR collaborative system in industrial VOCs and NOx collaborative management solution
Definition of Selective Catalytic Reduction
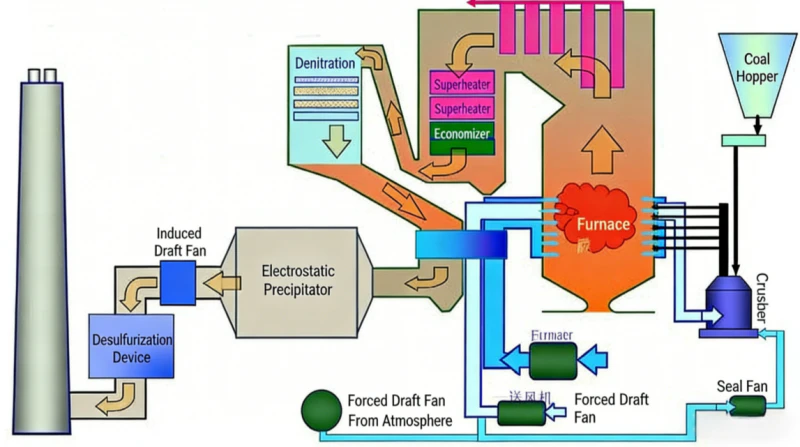
The SCR denitrification system mainly consists of SCR reactor, flue gas heating mixing system, ammonia storage and injection system, pulse soot blowing and control system, etc. The SCR reactor is the core equipment of the flue gas denitration system. It is arranged vertically, and the flue gas flows vertically downward. An air flow distribution device and a baffle are installed at the entrance to ensure smooth flue gas flow and uniform air flow distribution, creating conditions for the smooth progress of the denitration reaction. A four-layer steel welded frame is installed in the reactor to carry the catalyst that accelerates the denitrification reaction rate and provides sufficient space for the denitrification reaction.
The Necessity of RTO-SCR Collaborative Governance
Compound pollution: Most industrial processes emit VOCs and NOx at the same time
Policies are becoming stricter: the EU IED directive and China’s ultra-low emission standards require simultaneous control
Temperature matching: RTO outlet temperature (300-500℃) is highly matched with SCR optimal reaction temperature (280-400℃)
Cost economy: sharing flue and control system, reducing total investment by more than 30%
Comparison of RTO-SCR Synergistic Advantages
Key Technologies of RTO-SCR System
Recommended Solution: Customized V-Ti catalyst (vanadium content: 2-3%, WO₃ content: 8-10%), adapted to RTO flue gas characteristics.
Application Case
Take the chemical industry as an example
Project background
• Nature of the enterprise: annual output of 8,000 tons of pesticide intermediates (containing chlorobenzenes and pyridine compounds)
• Original treatment process: three-tower RTO (processing air volume 150,000 Nm³/h)
• Operating status: 24-hour continuous production, 8,000 hours of annual operation
• Geographical location: Shangyu Economic and Technological Development Zone, Shaoxing, Zhejiang
core issues faced
NOx emission exceeds the standard: NOx emission after RTO operates alone is 220-280 mg/Nm³
Implement new standards: NOx ≤ 100 mg/Nm³ (special emission limit) required from 2022
Environmental protection penalty risk: facing daily fines of 100,000-1 million yuan
How to solve
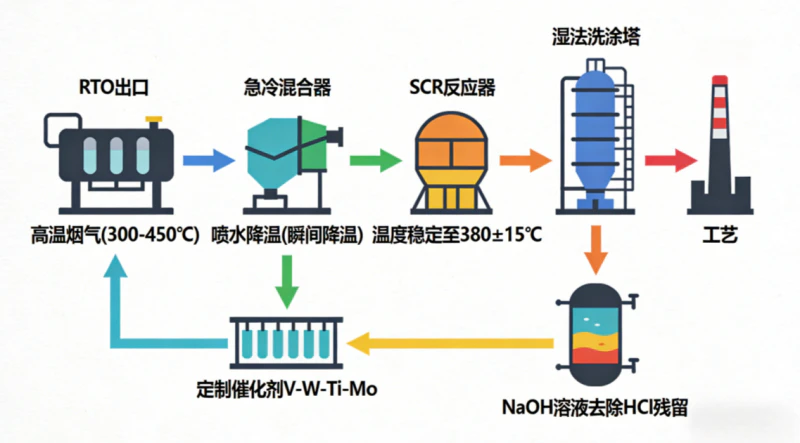
1. Process route optimization design
2. Use with SCR reactor
You can also provide problems faced by your products and we will provide you with solutions
Operating Cost Comparison
FAQ
What is the typical VOC destruction efficiency of EVER-POWER RTOs?
99% DRE for streams <10,000 ppm, verified by EPA Method 25A.
How does RTO compare to SCR for emissions control?
RTO targets VOCs/HAPs (thermal oxidation); SCR reduces NOx (catalytic, 90% efficiency). Hybrid setups achieve 95% total abatement.
What maintenance cycle is recommended for ceramic media?
Annual inspection; replace every 10-15 years (20,000 cycles) under ISO 14001.
How much heat recovery can I expect in Brazilian ag applications?
97% at 50,000 Nm³/h, recovering 600 kW for dryer preheat per CONAMA 436.
What torque rating is needed for rotary valve drives?
2,000-4,500 Nm, with 1:25 ratio for 1,500 RPM inputs
Does your RTO comply with China GB 37822-2019?
Yes, <50 mg/Nm³ VOCs; certified for 20% market growth in 2025.
Can RTOs handle mining dust loads?
IP65 rating; pre-filters for PM10 >500 μg/m³, 98% uptime.
What is the payback period for a 100,000 Nm³/h unit?
18-24 months via 65% fuel savings ($200,000/year).
How to integrate with existing gearboxes?
Direct SAE flange; 95% match rate, no mods needed.
What warranties cover media and valves?
5 years/50,000 hours; prorated for site conditions.