Katalytisk oksidasjonsmiddel
Low-temperature and high-efficiency carbon monoxide purification solution

CO Technology Overview
A catalytic oxidizer (CO) is an advanced waste gas treatment device that uses a catalyst to oxidize carbon monoxide (CO) and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O) at relatively low temperatures (300-500°C). Compared with thermal oxidation, catalytic oxidation technology significantly reduces energy consumption and operating costs, and is particularly suitable for treating low-to-medium concentration, high-volume CO waste gas.
Working Principle
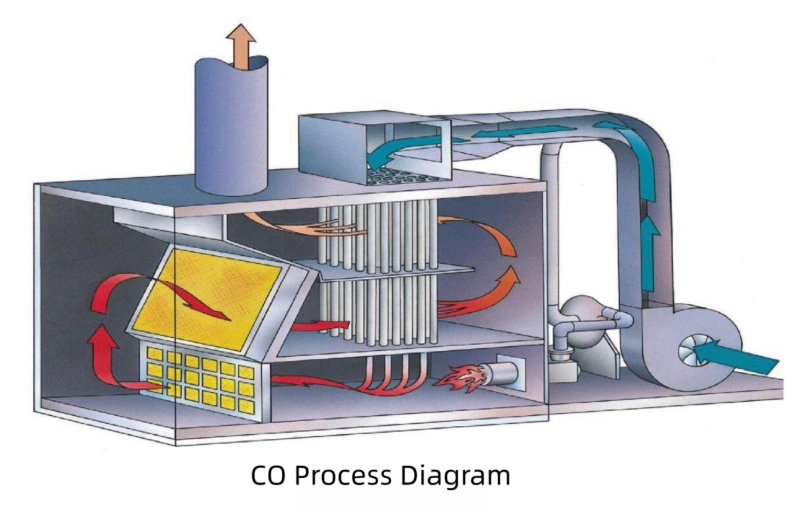
Catalytic oxidation achieves efficient CO purification through four steps:
- Exhaust gas preheating: Exhaust gas is preheated to the catalyst ignition temperature via a heat exchanger.
- Catalytic oxidation: An oxidation reaction occurs on the catalyst surface: 2CO + O₂ → 2CO₂
- Heat recovery: The heat of reaction is recovered via a heat exchanger to preheat the inlet gas.
- Purified emission: The compliant gas is emitted through a chimney after catalytic oxidation.
Why choose Catalytic Oxidizer?
|
Advantage Feature < |
Catalytic Oxidizer (CO) < |
Traditional Thermal Oxidizer (TO) < |
RTO
< |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | 300-500°C | 760-1200°C | 760-950°C |
| Energy Consumption | Reduced by 40-70% | High | Extremely low (at high concentrations) |
| Startup Time | 15-30 minutes | 1-2 hours | 45-90 minutes |
| Space Requirement | Compact, saves 30-50% | Relatively large | Moderate |
| Suitable Concentration | 100-5,000 ppm | High concentration | Wide range |
Our catalytic oxidation system ensures compliance with:
USA
- EPA Method 25A for CO
- EPA Method 25 for VOCs
EU
- EN 13649 sampling standard
- Compliant with the IED Directive
China
- GB 16297-1996
- DB11/501-2017 (Beijing local standard)
Typical Application Scenarios
Automobile Manufacturing and Painting
- Drying oven exhaust gas: CO concentration 200-800ppm, containing VOCs
- Welding fumes: Local exhaust treatment
- Challenges: Large air volume, fluctuating concentration, contains siloxanes
- Solution: Front-end adsorption concentration + catalytic oxidation system
Printing and Packaging
- Flexographic and gravure printing exhaust gas: alcohols, esters, solvents, containing CO
- Complex process exhaust gas: a mixture of multiple pollutants
- Solution: specialized anti-silicon catalyst, periodic regeneration process
Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing
- CVD process exhaust gas: Contains silanes and CO, easily forming silica.
- Solution: Two-stage pretreatment + high-temperature catalyst.
- Special design: Prevents dust ingress, protecting the catalyst.

Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals
- Reactor exhaust: intermittent emission with large concentration variations
- Solvent recovery tail gas: low concentration of CO and VOCs
- Solution: buffer system + adaptive control catalytic oxidation


Food processing
- Drying and baking exhaust gas: contains aldehydes and CO, high humidity
- Challenge: Contains grease and dust, easily contaminating the catalyst
- Solution: High-efficiency filtration + waterproof catalyst coating


Case Studies
🏭 Large Automobile Painting Plant Drying Oven Exhaust Treatment
📋 Project Background
Exhaust gas from painting line drying oven in an automobile manufacturing plant
Air volume: 80,000 Nm³/h
🔬 Exhaust Gas Characteristics
- CO: 300-600 ppm
- VOCs: 200-400 mg/Nm³ (mainly n-hexane, xylene)
- Temperature: 120-150°C (partially preheated)
- Contains trace amounts of siloxanes (from sealants)
🔧 Solution
Pretreatment System:
- Electrostatic precipitator to remove overspray paint mist
- Activated carbon adsorption for siloxanes
- Bag filter for final filtration
Catalytic Oxidation System:
- Plate heat exchanger with 75% heat recovery efficiency
- Precious metal catalyst with 240°C ignition temperature
- Four-zone temperature control for optimized energy consumption
Intelligent Control System:
- Automatically adjusts burner power based on concentration
- Catalyst temperature protection logic
- Real-time energy efficiency monitoring and optimization
Operational Results
- CO removal efficiency: 99.2%
- VOCs removal efficiency: 98.5%
- Energy consumption: 45% more efficient than RTO方案
- Operating temperature:
- Inlet preheated to 320°C
- Reaction temperature 380°C
- Fuel consumption: 25 Nm³/h natural gas (average)
- Investment payback period: 1.8 years
- Annual operating cost savings: $120,000
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
Catalytic Oxidation Systems & Emission Control
Catalytic Oxidizers (CO) achieve pollutant oxidation at 300-500°C with the help of catalysts, while RTOs perform thermal oxidation at 760-950°C using heat storage ceramics. The core differences are:
- Energy consumption: CO saves 40-70% in fuel consumption
- Startup time: CO requires only 15-30 minutes, RTO needs 45-90 minutes
- Concentration suitability: CO optimally handles 100-5,000ppm, RTO suits a wider range
- Investment cost: CO systems typically cost 20-40% less than RTOs
Application recommendation: Choose CO for low-medium concentration, intermittent emissions; choose RTO for high concentration, continuous emissions.
We employ a three-level protection strategy:
- Front-end activated carbon adsorption (targeting siloxanes)
- Electrostatic precipitation + bag filtration (removing dust)
- Siloxane online monitoring system
- Silicone-resistant formulated catalyst (with silicon scavenger added)
- Layered design: protective layer + reaction layer
- Regular high-temperature regeneration procedure (650°C to remove deposits)
- Bypass system (automatic switching during high silicon levels)
- Catalyst activity monitoring system
- Predictive maintenance algorithm
Practical case: A Dutch automotive painting plant using this solution extended catalyst life from 6 months to 3 years.
Special design is required to prevent acid corrosion and dioxin formation:
- Material upgrade: Reactor uses Inconel 625 or Hastelloy C-276
- Temperature control: Maintain above 850°C to ensure complete decomposition
- Post-treatment: Quench tower + caustic washing tower (neutralizing HCl/HF)
- Monitoring requirements: Continuous monitoring of HCl, HF and dioxin precursors
- Compliance guarantee: Meets Dutch BAT conclusion documents for halogen-containing exhaust gases
Our system incorporates four compliance modules:
- CO analyzer (EN 15267-3 certified)
- VOC online monitoring (compliant with EN 13649)
- Data recording meets NTA 8075 standards
- Automatic generation of quarterly emission reports
- Automatic alarm and event recording for exceedances
- Electronic reports directly connected to environmental department systems
- Annual third-party performance verification
- BAT compliance statement documents
- Complete operation and maintenance records
- Regulatory dynamic tracking service
- Regular software updates
- Annual compliance audit
Required certifications include:
- ATEX explosion-proof certification (Zone 1 & Zone 2)
- PGS 28 safety distance compliance certificate
- CE marking (Machinery Directive, Pressure Equipment Directive)
- SIL 2 Safety Integrity Level certification
- NEN-EN-ISO 13702 emergency system certification
Additional service: We provide full certification application assistance, reducing certification time by an average of 60%.
Typical economic analysis (30,000 Nm³/h system):
- Normal operating conditions: 3-5 years (24,000-40,000 hours)
- Severe operating conditions: 2-3 years (with regeneration maintenance)
- New catalyst cost: €45,000-€75,000 (approximately 15-25% of system)
- Regeneration service: €15,000-€25,000 (restores 90%+ activity)
- Spent catalyst recycling: €5,000-€10,000 return value (precious metal recovery)
- Activity monitoring package (3 months advance warning)
- Regeneration service contract (extends service life by 50%)
- Trade-in program (30% discount on new catalyst)
We provide intelligent buffering solutions:
At low concentrations (<500ppm):
- Reduce preheating temperature to 280-320°C
- Decrease fan frequency
- Enter energy-saving standby mode
At high concentrations (>2,000ppm):
- Automatically activate cold air blending
- Maximize heat recovery
- Start excess heat utilization system
- Exhaust gas buffer tank (15-30 minutes buffering capacity)
- Adsorption concentration rotor (concentrates low concentrations 10-20 times)
- Multi-reactor parallel design (adapts to production fluctuations)
Typical energy recovery solutions:
- Hot air recovery (simplest):
- Temperature: 150-250°C
- Applications: process preheating, space heating
- Efficiency: 60-75%
- Hot oil system (medium temperature):
- Temperature: 200-300°C
- Applications: process heating, steam generation
- Efficiency: 70-80%
- Steam generation (high temperature):
- Pressure: 4-10 bar
- Applications: process steam, power generation
- Efficiency: 75-85%
- Organic Rankine Cycle power generation:
- Power generation efficiency: 8-15%
- Investment payback period: 3-5 years
- Suitable for: >10,000 Nm³/h large systems
Economic benefit example:
Processing capacity: 50,000 Nm³/h
Exhaust gas temperature: 400°C reduced to 150°C
Recovered heat: 4.2 MW
Annual benefit: €150,000-€250,000 (subject to natural gas price fluctuations)
Based on European automotive plant experience, recommended solutions:
- VOC: 200-800 mg/Nm³ (contains benzene series, esters)
- CO: 100-400 ppm
- Siloxanes: trace amounts (from sealants)
- Operation mode: intermittent, following production rhythm
- Direct catalytic oxidation (suitable for small-medium scale):
- Investment: €300,000-€500,000
- Energy consumption: 25-40 Nm³/h natural gas
- Features: simple and reliable, easy maintenance
- Zeolite rotor + catalytic oxidation (suitable for large air volume):
- Investment: €800,000-€1,200,000
- Energy consumption: reduced by 60-70%
- Features: ultra-high concentration processing capacity
- Hybrid system (RCO + waste heat utilization):
- Investment: €1,000,000+
- Features: energy self-sufficient, zero fuel consumption
Success case: A Mercedes-Benz painting plant in the Netherlands adopted solution 2, achieving:
65% energy reduction
VOC removal efficiency >99%
Annual savings of €180,000
Dual certification by German VDA and Dutch environmental authorities
