Coal Chemical Waste Gas Treatment Solutions
Hendrerit augue morbi ligula volutpat egestas netus libero nullam, montes himenaeos a dis mattis pharetra. Odio suscipit vestibulum ornare volutpat mus lacinia sem fames, praesent in vivamus mauris habitant maecenas sapien turpis diam
Low-temperature methanol wash process: This process uses cold methanol as an absorption solvent. Leveraging methanol’s high solubility for acid gases at low temperatures, it removes acid gases—primarily CO₂ and H₂S—from the feed gas.
- Waste gas components: Methane, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, light hydrocarbons
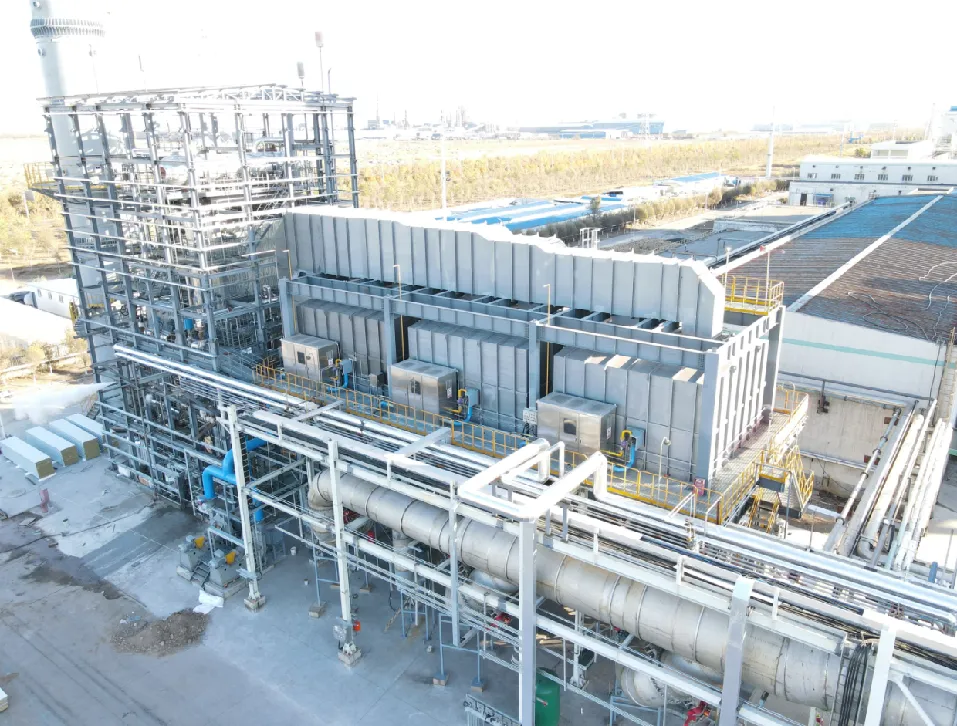
- Process solution: Air distribution system + rotary RTO + waste heat recovery (steam heat recovery)
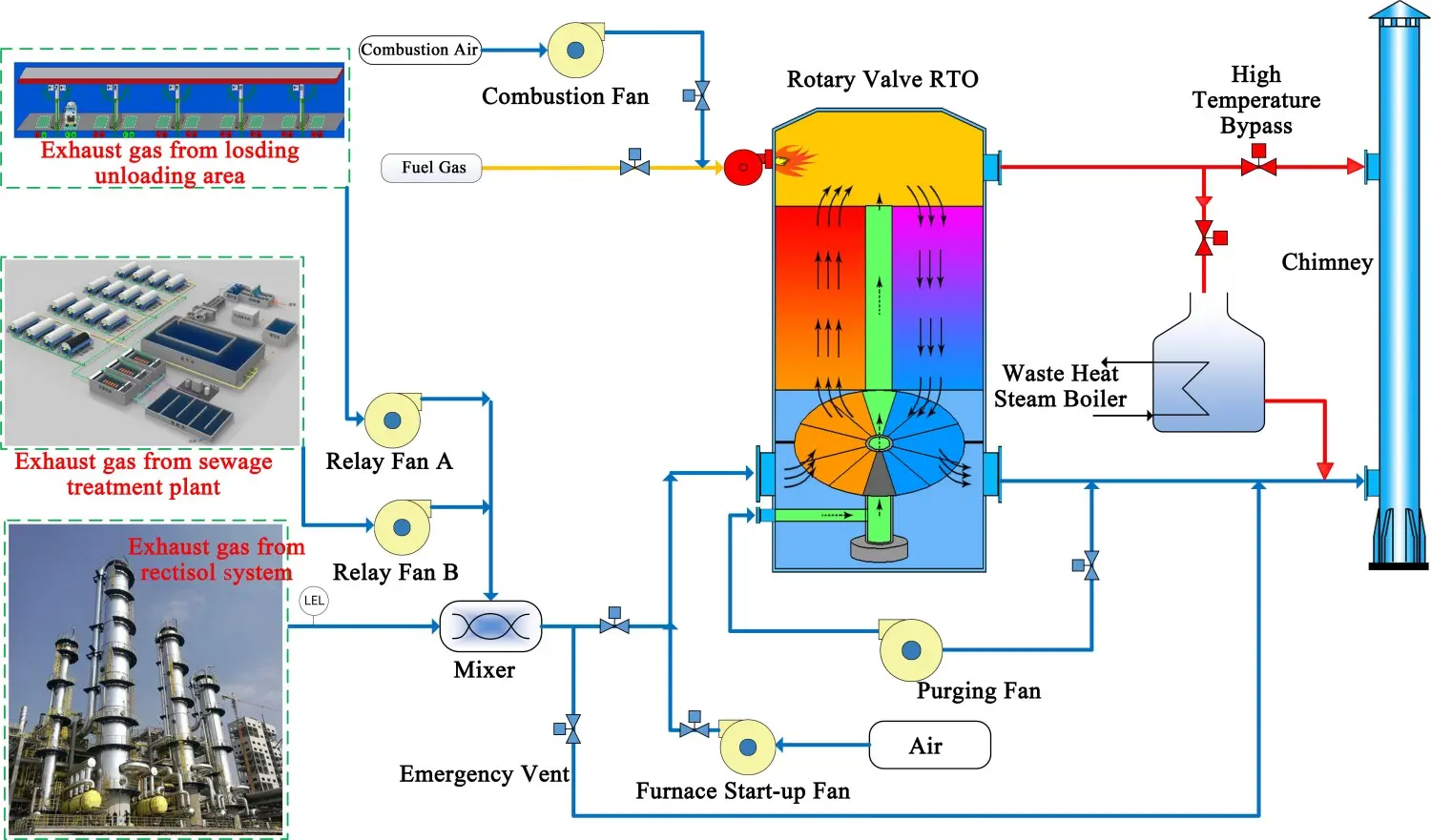
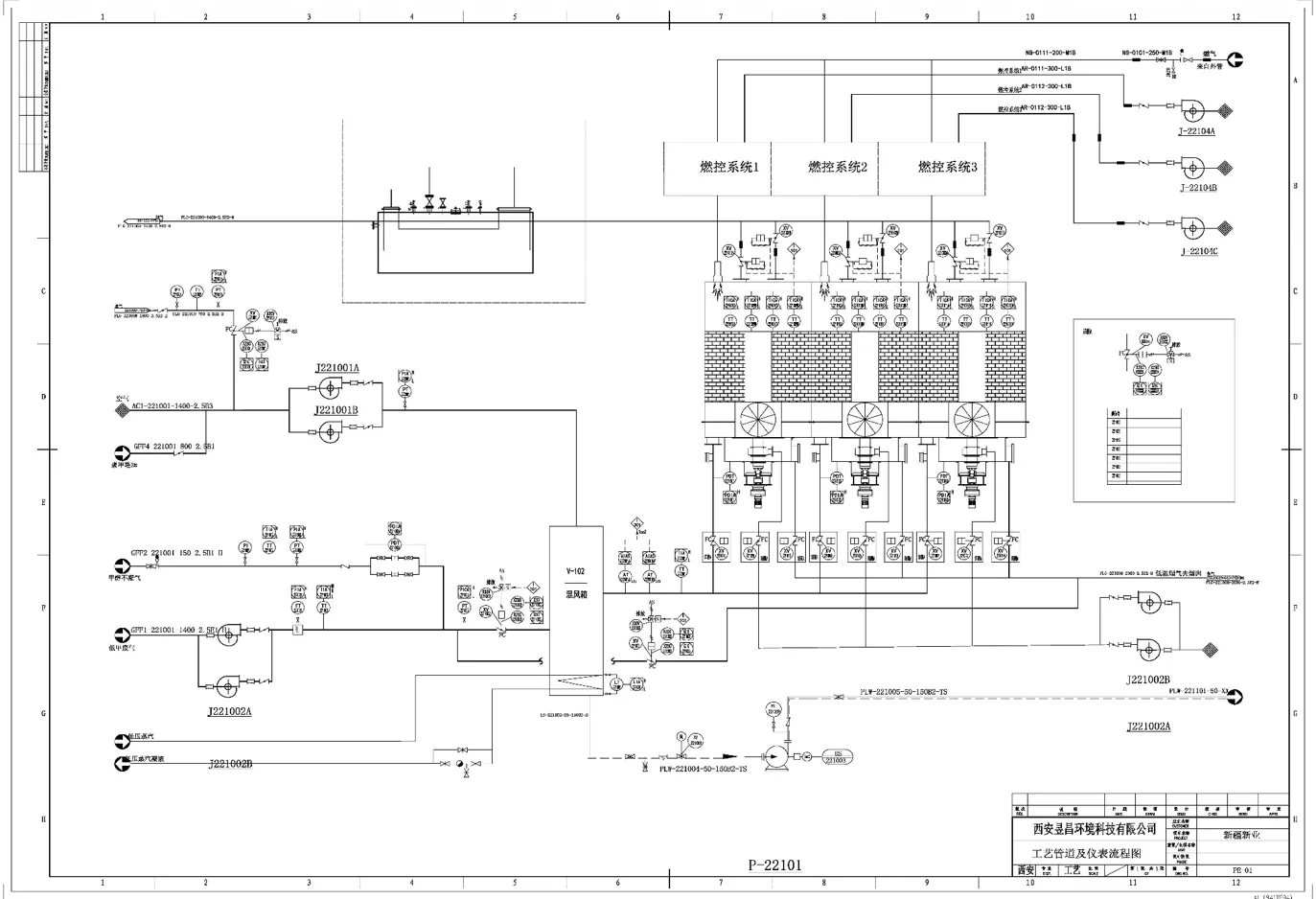
VOCs treatment process flow chart for the coal chemical industry's low-temperature methanol scrubbing industry
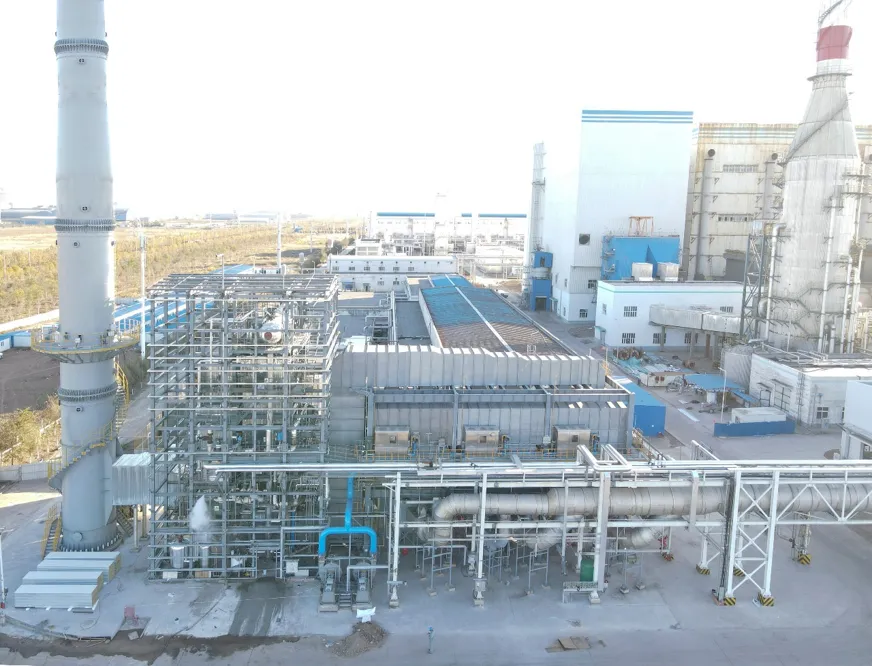
Process Scheme
To effectively handle this associated gas, an integrated treatment strategy has been established, encompassing key stages including gas-liquid separation, desulfurization, pressure stabilization, oxygen enrichment, and Regenerative Thermal Oxidation (RTO). Each phase is essential for converting the raw gas into a more controllable and eco-friendly form.
1. Gas-Liquid Separation
The initial phase separates gaseous and liquid components extracted from fire flooding outputs. Removing water, oil, and condensates is critical to avoid interference in downstream processes, enhance treatment efficiency, and allow separate recovery of valuable hydrocarbons or reduction in waste volume.
2. Desulfurization
The gas then undergoes desulfurization to eliminate sulfur compounds such as hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) and sulfur dioxide (SO₂). These substances are environmentally hazardous, corrosive, and pose operational risks. Methods like absorption, adsorption, or chemical conversion are used depending on gas composition and target purity, ensuring compliance with emission regulations and improving safety.
3. Pressure Stabilization
Next, the gas passes through a pressure stabilization unit to normalize variations. Steady pressure is crucial to maintain consistent flow and provide optimal conditions for subsequent treatment stages.
4. Oxygen Supplementation
Controlled oxygen is introduced to improve the combustibility of the gas stream, facilitating efficient oxidation in downstream thermal processes. This step is finely tuned to support complete combustion—boosting energy recovery and reducing harmful emissions while prioritizing operational safety.
5. Regenerative Thermal Oxidation (RTO)
In the final phase, the conditioned gas enters the RTO unit, where high-temperature oxidation breaks down volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other pollutants into carbon dioxide and water vapor. RTO systems typically achieve destruction efficiencies exceeding 95%, and the process incorporates heat recovery to significantly enhance the overall energy efficiency of the operation.